What Are The Main Causes Of Bleeding Gums?
What Are The Main Causes Of Bleeding Gums?
Bleeding gums are blood that appears on your toothbrush, dental floss, or in your mouth after eating. It is a common sign of gum inflammation and can range from an occasional bleed after aggressive cleaning to ongoing bleeding that signals disease. This post explains the main causes of bleeding gums, how dentists diagnose the problem, treatment choices, prevention tips, and when to seek urgent care.
Many people worry when they notice bleeding gums in Manhattan, NY or elsewhere. Whether you have a one-time issue or repeated bleeding in Greenwich, CT, learning the cause helps you get the right care quickly.
What Are Bleeding Gums?
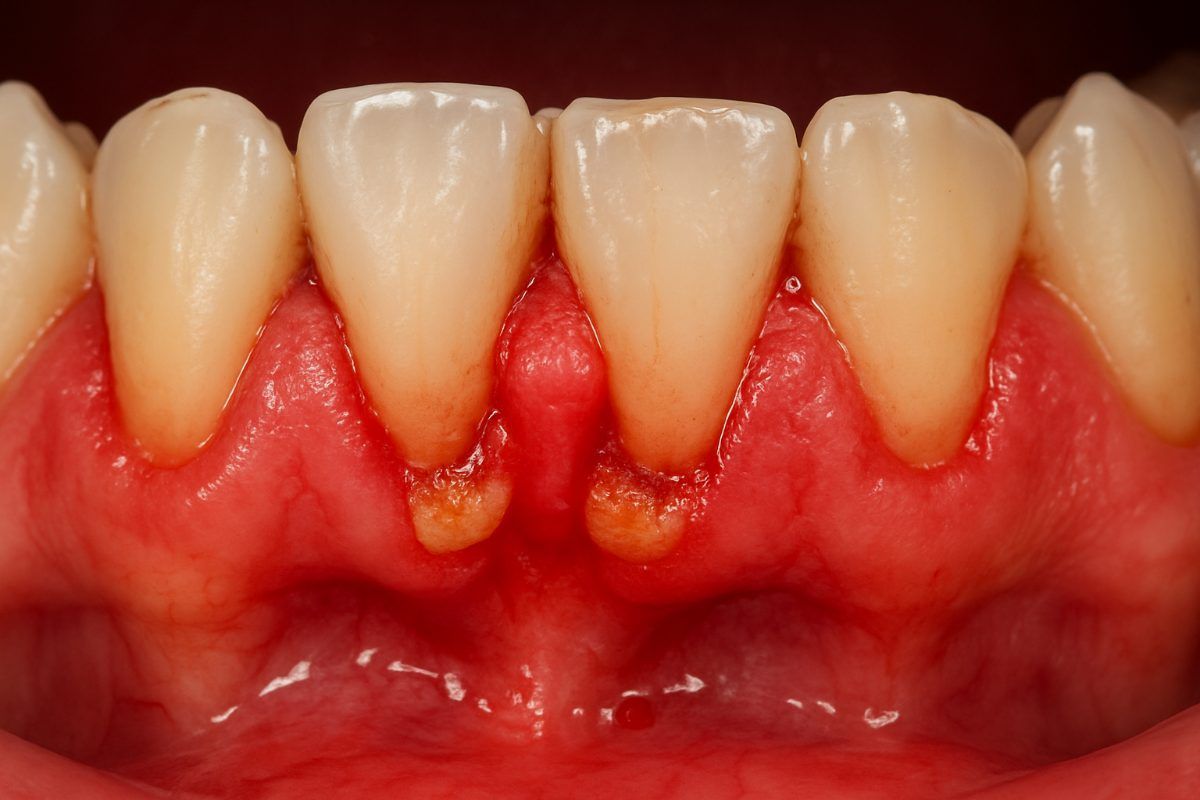
Bleeding gums happen when the soft tissue around teeth becomes inflamed or damaged. Occasional bleeding after hard brushing is different from ongoing bleeding, which usually means infection or another health issue. Early attention can stop damage to gum tissue and bone and prevent tooth loss.
If you notice bleeding gums in Greenwich, CT that happens more than once or is getting worse, schedule an exam. Persistent bleeding often needs professional treatment, not just better home care.
Common Causes Of Bleeding Gums
Plaque Buildup And Gingivitis
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. When plaque sits at the gumline, it causes irritation and inflammation called gingivitis. Inflamed gums are tender and bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing. Preventing plaque buildup is the first step to stopping bleeding gums in Manhattan, NY.
Periodontitis (Advanced Gum Disease)
If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis. This stage damages the tissue and bone that support teeth, creating deep pockets where bacteria hide. Periodontitis can cause chronic bleeding, loose teeth, and bone loss. Recognizing periodontitis early improves outcomes for people experiencing bleeding gums in Greenwich, CT.
Trauma From Brushing Or Flossing
Using a hard toothbrush, scrubbing too hard, or flossing aggressively can cut or irritate gums. New dental work or a sharp filling edge can also cause localized bleeding. Switching to a soft brush and using gentle technique often stops trauma-related bleeding gums.
Medications And Medical Conditions
Certain medicines, such as blood thinners and some anticoagulants, raise the chance of bleeding. Health conditions like diabetes or blood disorders can also make gums more likely to bleed. Always tell your dentist about medications and medical history when you have bleeding gums.
Hormonal Changes
Hormone shifts during pregnancy, puberty, or menopause increase blood flow to gums and make them more reactive to plaque. This is why pregnancy gingivitis and bleeding gums are common and need careful monitoring.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Low levels of vitamin C or vitamin K can make gums weaker and more prone to bleeding. A balanced diet or targeted supplements can help when deficiencies are identified.
Smoking, Vaping, And Poor Oral Appliances
Tobacco use and vaping alter gum health and reduce healing. Ill-fitting dentures or rough dental work can rub and inflame tissue, causing bleeding. Properly fitted appliances and quitting tobacco lower the risk of bleeding gums in Manhattan, NY and Greenwich, CT.
Risk Factors That Increase Bleeding Gums
- Age — gum disease risk rises with age.
- Family history — genetics can affect gum health.
- Dry mouth — less saliva means more plaque buildup.
- Stress and autoimmune disease — these weaken immune response.
- Uncontrolled diabetes — raises infection and bleeding risk.
How Dentists Diagnose The Cause Of Bleeding Gums
Dentists use a combination of exam steps to find the cause of bleeding gums:
- Clinical exam and periodontal probing to measure pocket depths and bleeding on probing.
- Dental X-rays or CBCT 3D imaging to check for bone loss or hidden problems.
- Review of medical history, current medications, and lifestyle factors.
- When needed, salivary or blood tests and referrals to a physician for systemic issues.
Treatment Options For Bleeding Gums
At-Home Care
Most early bleeding stops with improved home care: brush twice daily with a soft brush, floss or use interdental cleaners daily, and rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash if recommended. Gentle, consistent care reduces plaque and bleeding gums.
Professional Cleaning
Professional scaling and root planing remove hardened plaque and bacteria below the gumline. This deep clean is often the next step when bleeding persists despite good home care.
Minimally Invasive And Advanced Therapies
Advanced options include laser-assisted periodontal therapy (LANAP) to reduce bacteria and promote reattachment, platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) to speed healing, and targeted antimicrobials. These therapies help control bleeding gums in Manhattan, NY and support tissue regeneration.
Surgical Care And Reconstruction
When pockets and bone loss are severe, surgical approaches like flap surgery, grafting, or regenerative treatments may be necessary to restore support and stop chronic bleeding.
Addressing Underlying Health Issues
Coordinating care with your primary doctor is key when bleeding gums relate to diabetes, blood disorders, or medication effects. Managing the underlying condition often improves gum health.
Preventing Bleeding Gums — Daily Habits
- Brush twice daily with a soft brush and gentle strokes.
- Floss daily or use interdental brushes to remove plaque between teeth.
- Quit tobacco and limit vaping.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and K.
- See your dentist regularly for cleanings and exams.
- Manage chronic health conditions and stress.
When Bleeding Gums Are A Red Flag — Seek Care Now
Get prompt dental or medical care if you have heavy or prolonged bleeding, pus, sudden loose teeth, severe pain, fever, or rapid changes in gum color or shape. These signs can indicate serious infection or systemic problems that need urgent treatment.
Why See A Biologic Periodontist For Bleeding Gums?
A biologic periodontist looks beyond symptoms to treat root causes and whole-body health. This approach uses minimally invasive, toxin-free methods and aims to restore natural healing and reduce systemic inflammation that links oral disease to overall health.
What Tetrahealth Offers
Tetrahealth provides advanced diagnostics and biologic therapies for bleeding gums, including:
- Comprehensive imaging and ROSA™ screening to assess oral-systemic health.
- OralDNA® salivary testing to identify harmful pathogens driving inflammation.
- LANAP and CO₂ laser therapies to treat periodontal disease with less tissue trauma.
- PRF to speed healing after procedures and promote tissue regeneration.
- Ozone therapy, biocompatible materials, and zirconia implant options for toxin-free care.
Looking For Help With Bleeding Gums In Manhattan, NY Or Greenwich, CT?
If you have persistent bleeding gums in Manhattan, NY or bleeding gums in Greenwich, CT, schedule an evaluation to find the cause and get a personalized, biologic treatment plan. Early care can stop progression, preserve your teeth, and support whole-body health.
Contact Tetrahealth to book an exam with a biologic periodontist and learn about safe, minimally invasive options tailored to your needs.